Jargon buster - dental implant terminology explained
Term |
Definition |
|---|---|
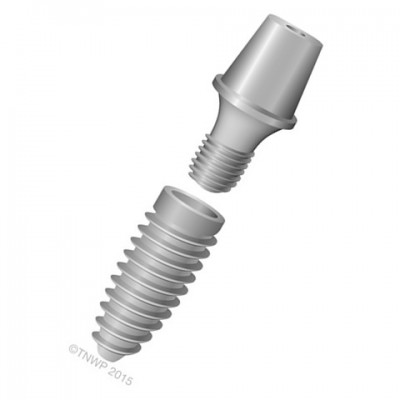
| Abutment |
An abutment is a connector and is placed on or built into the top of the implant. It connects the implant to the crown. |
| All-on-4® |
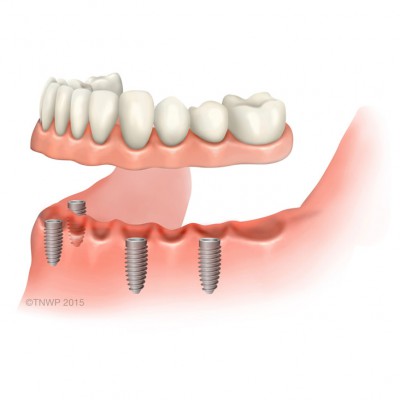
All-on-4® treatment is a technique using four dental implants in the upper or lower jaw to secure a permanent set of natural looking replacement teeth. Toothless (edentulous) patients and potentially edentulous patients, can have a whole arch of failing teeth replaced with dental implants. The implants support a full arch (upper or lower jaw) of fixed, non-removable replacement teeth. Patients with insufficient bone in their jaw can benefit from All-on-4® implants without the need for bone grafts. Four implants are placed and by tilting the two posterior ones, longer implants can be used. This increases implant contact with the bone avoiding the need for bone augmentation. |
| Allograft | Human bone obtained from a licensed tissue bank. This type of bone graft provides an alternative for patients who want to avoid the surgical procedure required for an autograft, or when large blocks of bone are needed. |
| Alloplastic grafts | Man-made grafts from synthetic materials, the properties of which mimic natural bone. They work by stimulating the body to form natural bone at the site of the dental implant. |
| Alveolar bone |
Teeth are anchored to the jaw by the alveolar bone. This is the thickened ridge of bone containing the tooth sockets (dental alveoli). The alveolar bone is the primary support for teeth. |
| Anterior teeth | The six upper and six lower front teeth. The teeth that can be seen when a person smiles. They are some of the first baby teeth to fall out and be replaced by permanent, adult teeth. |
| Autograft | A bone graft taken from the patient’s own body. Autogenous bone grafting is often the first choice for a dentist, because autografts provide the best results. The bone may be taken from behind the back teeth in the lower jaw or from the chin. Sometimes it is taken from the hip or shinbone (tibia). |
| Bone augmentation | Describes a variety of procedures used to build bone so that dental implants can be placed. |
|
Bone grafting
|
When jaw bone is deficient, natural or synthetic bone can be used to increase the amount of bone in that area. It also preserves and prevents further bone loss. Grafting can be performed at the time of implant placement, or as a separate procedure several months before. |
| Bone loss | Bone loss can be caused by trauma, inflammation of the gums and bone due to bacteria (peridontitis). Tooth extraction may also cause bone loss. Gradually the height and thickness of the bone reduces due to the natural healing process, lack of chewing and stimulation. |
| Bone resorption | A process which takes place when a tooth has been lost and there is no tooth root left to anchor or stimulate the surrounding bone. The more teeth lost, the more function and bone lost. This can lead to the contour of the jaw changing shape, often causing a sunken mouth and face. After the alveolar bone is lost, the bone beneath it, the basal bone, can also begin to resorb (shrink away). |
| Bone ridge (Alveolar bone) | The thickened ridge of bone in the jaw that contains the tooth sockets. |
| Bone volume |
A patient’s bone volume will be assessed by a dentist. Insufficient bone volume or quality to support dental implants can be overcome with bone grafting which creates a firm base to install an implant or implants. |
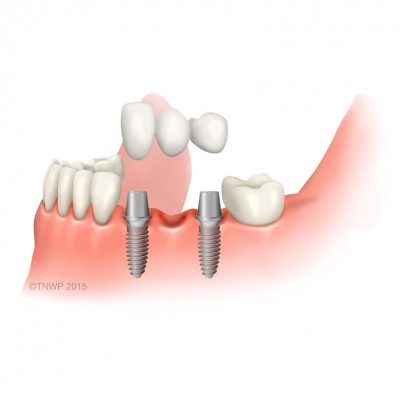
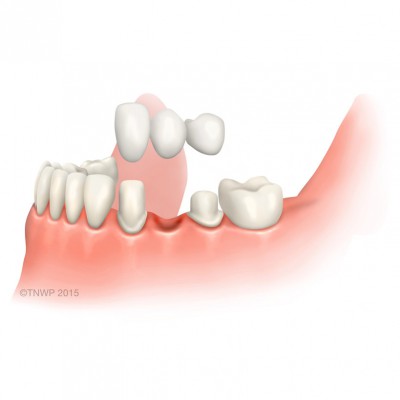
| Bridge | A dental bridge is a device that spans the gap created by one or more missing teeth. Artificial teeth are attached to other natural teeth or dental implants. There are two types of bridge. One that is glued in place (adhesive bridge) or supported by crowns (conventional bridge). |
| Bruxism | Bruxism is the medical term for grinding the teeth and clenching the jaw. |
| CAD/CAM |
CAD/CAM is an acronym for computer aided design and computer aided manufacturing. CAD/CAM technology is used by dentists and dental laboratories to provide patients with milled dental restorations, such as crowns, veneers, fixed bridges, dental implants, dentures and orthodontic appliances. |
| Canine |
There are two canine teeth in each jaw. They are the pointed conical teeth located between the incisors and the premolars. |
| Clinical consultation | A detailed, thorough examination which may involve various diagnostic procedures such as X-rays and CT scans. |
| Complete arch |
A complete arch refers to one of the two arches (crescent arrangements) of teeth, one on the whole of the upper jaw or lower jaw. |
| Computer-guided surgery | Computer technology, such as digital imaging and CT scan images is used by dentists to visualise the process in order to accurately fit dental implants. |
| Cone beam computed tomography scan | The cone beam computed tomography scan uses advanced x-ray techniques that allows the jaw bone to be seen in all three-dimensions. A CBCT scan will normally show all the information required by an implant dentist about the jawbone, including bone quantity and quality. |
| Crown | A crown is sometimes called a cap and is used to cover a damaged tooth or implant. A crown is a form of restoration which strengthens the tooth and closely replicates the appearance and function of your natural teeth. Crowns can be made from a variety of materials including porcelain and ceramic which can match the colour of natural teeth. They are also made from gold, acrylic and metal alloys. |
| Deciduous teeth | The first set of teeth, otherwise known as milk teeth or baby teeth. |
| Delayed loading |
Delayed loading is the delayed fitting of a replacement tooth after implant treatment. There is usually a waiting period of three to six months before a replacement tooth is fitted, to allow the gum to heal and the implant to integrate. This is the opposite of immediate loading, where the replacement tooth is fitted onto the implant at the same time as the implant is placed. |
| Dental arch |
The dental arches are the two crescent arrangements (curved shape) of teeth, one on each jaw, that make up a normal set of teeth. |
| Dentition |
The arrangement and condition of your teeth. |
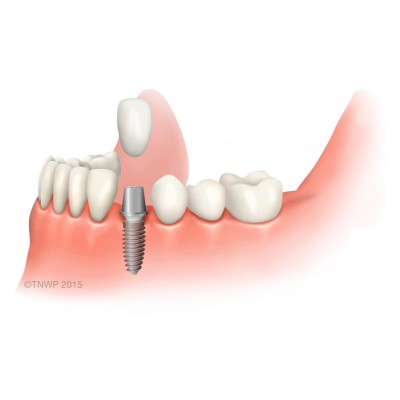
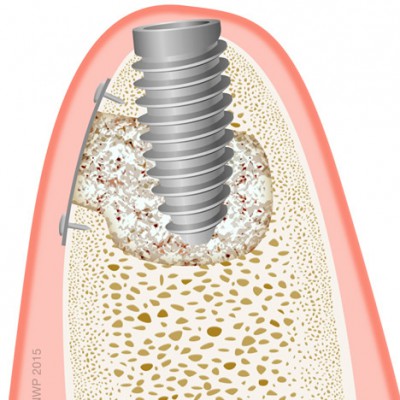
| Dental implant | Dental implants are the only permanent replacements for failing or missing tooth roots. Titanium supports replace the root of the tooth and hold false teeth such as single crowns, multiple tooth bridges or even full dentures in place. |
| Dentures | Dentures are a removable replacement for missing teeth. They are made from acrylic plastic and sometimes porcelain and metal. Partial dentures are used when some natural teeth remain and complete dentures are used when all teeth are missing. |
| Denture stabilisation | There are various ways of stabilising dentures. The most effective result is achieved with implants. Implants are inserted into the jawbone to anchor the dentures. |
| Edentulous | The medical term for toothless. People who are lacking teeth are either partially or completely edentulous. |
| Full arch | The crescent arrangements of teeth. Upper arch is called the maxillary and lower arch the mandibular. |
| General anaesthetic | The use of an injection or gas to render a person unconscious. This allows surgery to be performed while the patient is asleep, ensuring no pain or memory of the operation. |
| Gingiva | The soft tissue that covers the mouth. Also referred to as the gums. |
| Gingivitis | Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums and is the initial stage of gum disease. The gums around the teeth become very red and swollen. Often the swollen gums bleed when brushed. |
| Guided tissue regeneration and guided bone regeneration | Guided tissue regeneration (GTR) and guided bone regeneration (GBR), are surgical techniques that use biocompatible membranes to direct and regenerate the growth of new gum tissue and new bone at sites with insufficient volumes. |
| Hard tissue | Bone in the jawbone, maxilla (upper jaw) and mandible (lower jaw). |
| Healing abutment (sulcus former) | A healing abutment is a connector that shapes and contours the gum during the healing phase of dental implant treatment. |
| Hypoallergenic | Hypoallergenic means 'unlikely to cause an allergic reaction'. |
| Immediate implants | When a tooth is removed an implant is placed immediately into the extraction site. Depending upon the bone and soft tissue conditions around the implant, the surgery may be a one or two-stage procedure. This method is not suitable for all patients. |
| Immediate loading | This is a one-stage process where a tooth is fitted onto an implant which has been placed into a new, healing or healed extraction site. The implant and tooth are placed during only one visit. This is not suitable for all patients. |
| Implant placement | A surgical procedure to place implants performed by an implant dentist in a dental surgery. |
| Implant restoration | Once implants have been installed into the jaw they can be used to support a variety of replacement teeth known as restorations. These range from a single crown, small or large bridge or a removable overdenture. |
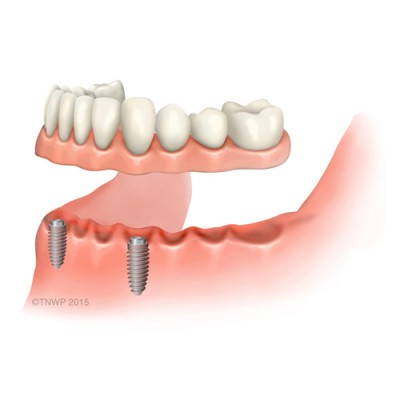
| Implant-retained denture | A denture which rests on the gum and gains support from the gum but is held in place by approximately four to five implants. |
| Implant-supported crown | Dental restoration that replaces a missing tooth. A permanent titanium root is inserted into the jaw after extraction. Then a replacement tooth (crown) is attached. |
| Implant-supported denture | Denture supported by and attached to implants. |
| Impression taking | A dental impression is used to produce a replica model of teeth and soft tissues. |
| Incisors | Incisors are the four front teeth, both top and bottom. They are the sharpest and help to cut up food with their thin edges. |
| Inferior alveolar nerve | Also known as the inferior dental nerve. It supplies sensation to the lower teeth. |
| Lower arch | The arch of teeth on the lower jaw (mandibular arch). |
| Malocclusion | A poor bite when there is not a normal fit between the upper or lower teeth. |
| Mandibular | Dental term meaning the lower jaw which holds the lower teeth in place. |
| Marginal bone loss | Marginal bone loss or marginal bone resorption is where bone in the jaw is lost (or shrinks away) due to lack of stimulation. |
| Maxilla | Forms the upper jaw and bone structure that supports all the upper teeth, parts of the eye sockets and lower sections and sides of the nasal cavity. |
| Maxillary sinus | The largest of the sinuses. The two maxillary sinuses are located above the teeth, to the sides of the nose and below the cheeks. |
| Maxillary teeth | There are 16 maxillary teeth which are along the top of the mouth. They have roots into the upper jawbone or maxilla. |
| Molar | Molars are the very back teeth. They are big, flat, teeth. They help to chew and grind food into small pieces. |
| Mucosa | The pink-red tissues (skin) that line the mouth. |
| Non-clinical consultation | A discussion to consider the options for treating dental problems and decide whether to proceed to a clinical consultation for implants. |
| Osseointegration | The process by which bone heals and fuses around an implant. |
| Overeruption | If a tooth is extracted, the opposing tooth may protrude into the missing space. This may result in root structure becoming exposed risking decay and inflammation. |
| Peri-implantitis | Peri-implantitis is an inflammatory disease marked by bacterial infection and loss of bone around the implant. Peri-implantitis can be compared to periodontitis in natural teeth. |
| Periodontal disease | Periodontal disease or periodontitis starts as gum disease and affects the gums, bone and other supporting structures of the teeth. Gingivitis usually precedes periodontal disease. Severe forms of the disease cause loss of supporting bone. It is caused by the bacteria which regularly collect on the teeth. |
| Platelet rich growth factor (PGRF) | A by product of blood that is exceptionally rich in platelets. It helps with blood clot formation and helps to heal wounds. The growth factors in PRGF stimulate stem cells to produce new tissue quickly which is why it is beneficial in the post-implant healing process. |
| Pontic | An artificial tooth. |
| Posterior teeth | These are the teeth in the back of the mouth. |
| Pre-molar | The pre-molars are located behind the canine teeth. They have a flat chewing surface to help crush food. |
| Prosthodontics | Prosthodontics is the area of dentistry providing carefully designed artificial or false appliances such as implants, crowns, bridges, veneers, inlays, onlays, complete and partial dentures. |
| Prosthodontist | Is an specialist in the replacement and restoration of teeth. |
| Pterygoid implants | Pterygoid implants are placed in the pterygoid plate, which is situated behind the cheekbone, when there isn't sufficient bone in the jaw, as an alternative to bone grafting. |
| Restoration | The term restoration refers to the false, replacement tooth which is attached to an implant. A restoration can involve a single tooth or several teeth. |
| Root filling or root canal treatment | Root canal treatment treats an infection in the soft tissue of a root canal system. This is done by removing the tissue containing the bacteria and filling the root canal. The tooth is then sealed with a filling or a crown. |
| Root fracture | Cracks that begin at the root of a tooth and move up towards the chewing surface. Extraction may be necessary or endodontic surgery. |
| Same day teeth | A process where replacement teeth can be installed in one day. Teeth in the upper and/or lower jaws can be removed, implants placed and a previously constructed bridge is permanently fixed to the implants. |
| Screw-retained bridge | A screw-retained bridge has direct connection to the implant with no additional abutment required. |
| Screw-retained denture | This is a fixed implant appliance for toothless patients. |
| Short span bridge | A bridge made for one missing tooth. The bridge spans the gap with two crowns secured to natural teeth with a false tooth in the middle. Both the crowns and false tooth are made from porcelain. |
| Soft tissue | Gums or gingiva |
| Soft tissue augmentation | A procedure that grafts gum tissue. This is necessary when gums have receded exposing more of the tooth or the tooth root. |
| Teeth in a day | A dental process designed to provide a complete new set of teeth (either top, bottom or both) in a day. This takes place at the dental practice, not at hospital. |
| Temporary denture | Temporary dentures are made before any extractions or surgery to remove damaged teeth. They are then placed immediately after surgery and will help maintain the shape of the face during the healing process. Gums may shrink as they heal, so permanent dentures are made after healing has taken place for an accurate fit. |
| Titanium |
Titanium is a biocompatible metal which is not harmful or toxic to the human body. Dental implants are usually manufactured from titanium. It also the metal of choice for artificial joints and is used for many other medical procedures. |
| Treatment plan | A written report of the implant work the dentist proposes to perform on a dental patient based on the results of the X-rays, examination, and diagnosis. Will include proposed timeframe and costs. |
| Upper arch | The upper arch of teeth is called the maxillary arch. The upper arch of teeth is immovable. |
| Xenograft | Bone grafts taken from animal sources, such as bovine (derived from cow) or porcine (derived from pig). |
| Zirconia | Zirconia is an alternative dental implant material made from oxidised zirconium powder known for its more natural look and hypoallergenic properties. |
| Zygomatic implants | Zygomatic implants are implants placed and secured in the cheekbone when there isn’t sufficient bone in the jaw, as an alternative to bone grafting. |